Clams, snails, slugs, oysters, squid, octopus, chitins, and so much more!
Characteristics of Mollusca
- 100,000 species!
- Most marine; some fresh water; some terrestrial
- triploblastic
- coelomates
- Most with bilateral symmetry

- a water-filled mantle cavity
- a rasplike radula
- Muscular foot
- the muscular foot can be modified depending on the class of mollusks. Some have a suction cup like foot on their belly, others have tentacles, and still others have the foot tucked into their shells.
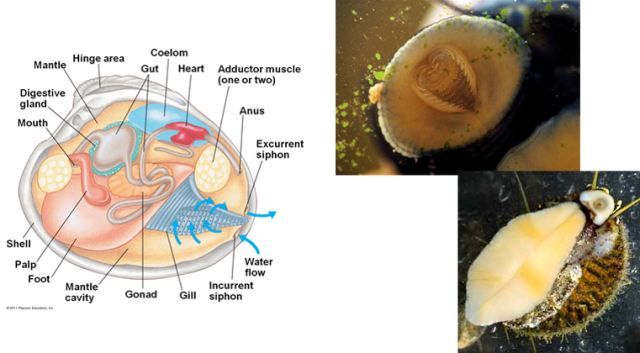

This bivalve has the muscular foot sticking out of the shells http://www.theseashore.org.uk
Cephalopods have a muscular foot modified into tentacles

Snail foot
http://www.molluscs.at
snails and slugs are known as “belly-foot” animals
- complete digestive tract
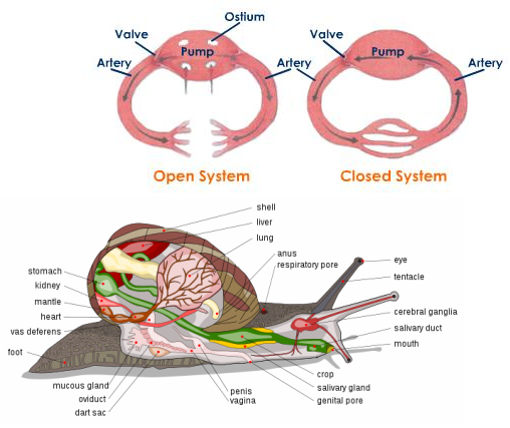
- most with open circulatory systems
- Cephalopods have a closed circulatory system
- Gills (sometimes protected in the shell) for respiration
- Nervous system:
- 2 pairs of nerve cords
- Small brain
- Support System
- Some with shells made of calcium carbonate
- Some internal and reduced (vestigial)
- Some lost all together
- Hydrostatic skeleton in others
- Some with shells made of calcium carbonate
Mollusca Diversity
There are 4 classes in the phylum Mollusca:
Class Polyplacophora- Chitins
- Chitons are oval-shaped marine animals encased in an armor of eight dorsal plates
- Muscular foot acts like a suction cup to grip rock,
- radula used to scrape algae off the rock surface

Chitin
“Tonicella-lineata” by Kirt L. Onthank. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons – http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tonicella-lineata.jpg#mediaviewer/File:Tonicella-lineata.jpg
Class Bivalve: Clams and their relatives
- Filter feeders
- 2 shells, strong muscles hold shells shut
- muscular foot is in the shell
- important in the environment because they clean water ways

More diversity in bivalves
http://www.uwlax.edu
Class Gastropoda: snails and slugs
- Gastropoda means “Belly foot”
- muscular foot is on the “belly” side of the animal
- One shell (or reduced and internal)
- Herbivores, carnivores and decomposers
- gills are often enclosed in the shell
- many have invaded land, others are marine or freshwater

Gastropod shells
http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu

moon snail
http://www.marinespecies.org
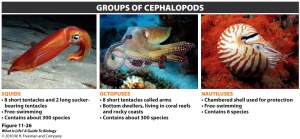
Class Cephalopoda: squid, octopus, and nautilus
- Distinct head, large eyes
- Carnivorous
- Crawl or use a jet stream of water to move
- muscular foot is divided into tentacles
Cephalopods are known for their intelligence. Here are some videos demonstrating this.
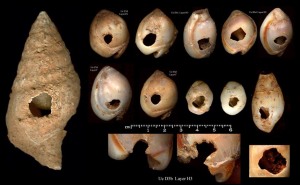
Mollusk on mollusk violence…
Gastropods eating other mollusks.
These round holes are a result of snails using their radula (rough, scraping tongue like structures) to scrape through the shells of other snails and bivalves.